
UNDERSTANDING ELECTRONIC DATA INTERCHANGE (EDI)
We’ve all worked with organizations (maybe your business is one of them) that still rely on phone calls, postal mail, or fax machines to complete everyday transactions. Orders come in via the phone or fax, the information is physically written down, and then the paper is handed to fulfillment to finish the request. While this process has served many businesses well for decades, it’s time for an update.
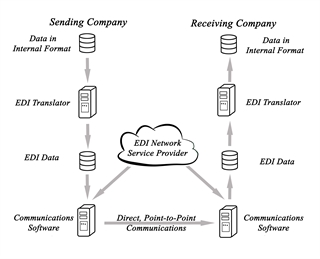
This is where electronic data interchange (EDI) comes in to play. EDI involves sharing documents via computer-to-computer interaction in a standardized format. This process replaces traditional communication methods, such as postal mail, fax, and email, with an entirely computer-based communication process.
If the situation detailed above were done with EDI, the orders would be entered in a computer by the customer, the computer would send the information to a computer on the organization’s side, then the data would be interpreted and passed off to fulfillment. This eliminates numerous internal steps, speeding up the process and increasing accuracy and reliability.
FOLLOWING EDI STANDARDS
Any business document can be shared via an EDI system, though the process is most commonly used for invoices, inventory reports, and purchase orders. Most EDI systems can be customized to the specific use your business needs.
After determining which processes to automate with EDI, you must decide which language the computers will speak. In order for both computers to communicate effectively, a standard language, often referred to as EDI standards, must be agreed upon at the beginning of the process. Several sets of EDI standards already exist for specific industries or countries, including EDIFACT (Electronic Data Interchange for Administration, Commerce and Transport), ODETTE (Organisation for Data Exchange by Tele-Transmission in Europe) and ANSI X12 (EDI standards set up by the American National Standards Institute). Many industries also create their own sets of EDI standards specific to niche groups or specific regions.
Deciding on which EDI standards you will follow is crucial, or the messages will be lost in translation. It is also important, if you are setting up an EDI system to communicate within an already established channel, that you are EDI compliant with their previously recognized standards.
CHOOSING AN EDI FORMAT
In addition to choosing which EDI standards you’ll follow, there are different EDI formats to choose depending on your specific use.
Direct EDI
Direct EDI creates a direct communication channel between a single organization and its partners. Often, this means an organization must establish many different channels, often with different EDI standards specific to the partner. The organization’s system must therefore be able to communicate following a variety of different standards in order to be EDI compliant.
Value Added Networks
Value Added Networks (VAN) are set up by a third party, and tend to be vertical specific. They allow for organizations to communicate with a wide variety of industry partners that are using the specific channel. Instead of setting up one line of communication for each partner, all parties connect to the EDI VAN, and the network interprets the data and sends it to the proper party. This allows organizations to manage a single EDI VAN, rather than multiple direct connections, and allows each party to use a different set of standards (as long as it can be interpreted by the EDI VAN). However, it could limit who is able to communicate with the organization, as they must be part of the EDI VAN for the connection to be successful.
WHY EDI?
For many businesses, EDI helps save time and resources. While incorporating any new process will be a learning curve for both internal employees and customers, in the long run, your organization will benefit in numerous ways, including:
Accelerated Growth
For companies looking to scale and grow, EDI is the only simple way to manage transactions in large volumes.
Reduced Processing Time
EDI cuts down on the time it takes to process a single order, allowing more orders to be processed each day.
Improved Accuracy and Efficiency
By cutting out internal employee interaction within the sales process, EDI improves accuracy and increases overall organizational efficiency.
Find the Right EDI Service Provider
Getting started with EDI is simple when you have an industry partner to guide you. The first step is to identify the processes within your organization that could be improved with EDI. When you’re ready to take that next step, give us a call.



